* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
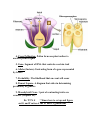
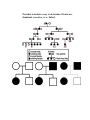
Ch. 9 Heredity & Genetics I. Basics A. Genetics- Study of heredity B. Heredity- transmission of traits from parent to offspring C. Inheritance- passing of traits by heredity II. Gregor Mendel- A monk from Brunn Austria trained in math + science A. His work- Identified seven diff. characteristics that occurred in one from or another (Pea plants) Ex. Tall vs. short pg 167 B. Conclusions- His work found the basis for our modern knowledge of genetics today!! * Key words in understating his work 1. Pure- Plants that are pure for a trait always produce offspring w/that trait 2. Pollination- Transfer of pollen from the anther (male) to the stigma of the female 3. Self Pollination- Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma in the same plant Know parts labeled on the picture below 4. Cross Pollination- Pollen form one plant anther to another plants stigma 5. Gene- Segment of DNA that controls a certain trait 6. Alleles (factors)-Contrasting form of a gene represented by letters 7. Probability- The likelihood that an event will occur 8. Punnet Square- A diagram that aides in determining probability in genetics 9. Monohybrid Cross- 1 pair of contrasting traits are crossed. (4 square PS) Ex. TT X tt **Know how to set up and figure out G and P ratios of the F1 and F2 generations 10. Dihybrid Cross- 2 pair of contrasting traits are crossed (16 square PS) Ex. RRYY x rryy **Know how to set up and figure out G and P ratios of the F1 and F2 generations 11. Homozygous- when both alleles (factors) are the same in a gene pair Ex. TT or tt (homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive) 12. Heterozygous- When both alleles are different in a gene pair Ex. Tt (Heterozygous dominant) 13. Dominant- The trait that is expressed 14. Recessive- “ “ “ “ hidden/ masked 15. Genotype- Actual genes that are present in its cell (LETTERS) Ex. TT, Tt, tt (Can Not See!!) 16. Phenotype- What traits are shown, what you actually see (WORDS) Ex. Tall, Tall, Short (Can See) 17. Parent Generation (P1)- original pure plants 18. First filial generation (F1)- the offspring of the P1 19. Second filial generation (F2)- the offspring of the F1 20. Incomplete dominance- 2 alleles are neither dominant nor recessive. They both contribute to the phenotype In 4 O’clock flowers Ex. Red x white flowers = pink RR = red Rr =pink rr = white 21. Co-dominance- Occurs when both alleles for a gene are expressing in a heterozygous offspring In horses Ex. Red x White fur color = Roan III. The sex chromosomes A. How sex is inherited 1. Determined by DNA- Specifically the x and y chromosomes. 2. Females are XX Male’s XY Therefore x y x x xx xx xy xy 50% chance of either having a boy or a girl. B. Twins 1. Identical- 1 egg and 1 sperm that divided after fertilization 2. Fraternal- 2 eggs and 2 sperm. No more closely related than brothers or sisters except they are the same age and developed under the same conditions. C. x- linked Traits- Traits that are carried on the Xchromosome These genes are carried by women and passed on to the male offspring Ex. Muscular dystrophy , color blindness, hemophilia, pattern baldness X-linked recessive example XH-No MD Xh-MD Female Male Expression XhXh XhYRecessive XHXh XHY Dominant XHXH Dominant Male only needs one recessive allele to express the recessive trait Example XHXh x XHY make a punnett square and find possible offspring 1. Carriers- have one normal allele that dominates the recessive allele 2. Pedigree- a chart or diagram that shows the passing of traits in a family by marriages and births. Provides scientists a way to determine if traits are dominant, recessive, or x- linked.