* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Artificial intelligence for video surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Visual search wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Transsaccadic memory wikipedia , lookup
Top-down and bottom-up design wikipedia , lookup
Visual extinction wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Visual memory wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Visual servoing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
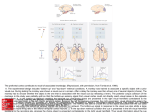
The prefrontal cortex contributes to recall of associated knowledge. (Reproduced, with permission, from Tomita et al. 1999.) A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The monkey had to choose whether the object is the one that is associated with the visual cue (by releasing a lever). The posterior corpus callosum of the monkeys in the study was partially split so that the bottom-up sensory signal from visual cortex could not directly reach visual areas in the opposite hemisphere. Source: 1. In the bottom-up retrievalScience, cue and choice object are presented in the right visual hemifield contralateral to the Learning and retrieval Memory,condition Principlesthe of Neural Fifth Editon recording site (electrode) in the left inferior temporal cortex. Because the left hemisphere processes the right visual field, visual information enters the Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available primary visual cortex in the same hemisphere as the recording electrode. The monkey was able to choose the correct object associated with the cue (data at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: April 30, 2017 not shown) indicating that bottom-up sensory signals are sufficient for retrieval. The bottom-up signal in response to the visual cue also elicits a large Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved increase in neural firing rate in the inferior temporal cortex neurons. 2. In the top-down retrieval condition the cue is presented in the left visual hemifield ipsilateral to the recording site, whereas the choice object is presented contralaterally in the right visual hemifield. Thus visual information about the cue