* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Daoism What is Daoism? Where was it founded? Who founded it
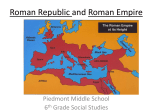
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Daoism What is Daoism? Where was it founded? Who founded it? When? - Devotion of energy to refelect on natural principle/order. - China – Lao Tzu 6th c. BCE (Chou – PWS) What is the Daodejing? - Sacred text (book of the way) – principles, teachings, songs, hymn What is The Dao? What does it do? What does it not do? - Dao-“the way” (of nature) - Does nothing but accomplishes everything - Water, empty space in pan, etc. What is Yin/Yang? How do these balance each other? Give an example of each side. - Opposites, good/bad, push against each other. Creates balance, harmony - Yang-light/yin-dark - (yang)Fire, day, strong, masculine/(yin)ice, night, feminine What wu wei? Describe this concept. -“without action” principle of knowing when to act and when to not act. Greeks Who were the Minoans? Where did they live? Who was King Minos? What is a minotaur? Who was Arthur Evans? What did he discover? What is Knossos? What is Linear A? - Early inhabitants of Greece, influenced by Egypt, Phoenicians, Mesops. - Lived on Crete island - Height: 2000-1450 BCE - Minos: legendary king, civ. Namesake - Minotaur: bull (head)/man (body) - A. Evans: discovered palace complex - Knossos: palace, labyrinth, big living spaces (1000 rooms), frescos (painting on plaster) - Linear A: Minoan language, symbols, not words, not deciphered. - Unknown demise: volcano, tidal wave from Thera Describe the geography of Greece. Why did this cause the Greeks to develop as they did? - Mountainous, diffic for agric. – isolation, varying cities/beliefs/cultures - Sea travel: easier, faster – results in trade Who were the Mycenaeans? Where did they live? Greatest king? Who was Heinrich Schliemann? - H.Schliemann(German): discovered the civ., and city of Troy (Anatolia) - Named after city – Mycenae (mainland Greece) - Influenced life in Med Sea. - 1500-1100 BCE - Agamemnon: greatest King – legendary for Trojan war - Fall: the mysterious “Sea People” What was the significance of the Greeks adopting the Phoenician alphabet? - Proof of trade/connection between civs - Becomes basis for Western languages - Sounds, not symbols Who was Homer? Why is he important? What story did the Iliad tell? Odyssey? - Greek storyteller - Credited with writing Trojan War story - Iliad: Trojan War (Greeks win, go Achilles!!) - Odyssey: Odysseus journey home - Epic poem, stories of bravery and heros What’s a Polis? When and where were they developed? - Greek city-state – center of Greek life - Emerges after “dark age” around 700BCE What was the purpose of the polis in Greek life? - Center of: religious, social, political life in Greece - Small, political unit, - develops slowly during dark age Who was a citizen in the Greek polis? Who wasn’t? - citizen: Greek males - noncitizen: women, children, slaves, foreigners, captured peoples What were the types of government in the poleis? - Monarchies: kings – heritary rule - Collective rule: nobility rule - Tyrants: political leaders – either good or bad (or both) Why were Athens and Sparta the most important poleis? - Most powerful - S: land power, war oriented - A: sea power, more cultured (arts, philosophy, drama, etc.) Why was there a strain between the rich and poor in 7th century Athens? - Trade bring prosperity to wealthy – rich get richer, poor stay poor Who was Solon? What were his reforms? Were they successful? - Wealthy/aristocrat, from Athens - Canceled land debt, separated Athens into classes, eliminated selling self to slavery, focus on olive trade - Successful: helped develop democracy in Athens What is democracy? What’s the difference between direct and representative democracy? - “rule by people” - Direct: all citizens have a say in the govt., make decisions - Representative: people chosen to make decisions (Greek assembly) What were some of the flaws with Athenian democracy? - Mainly rich people who had time to participate – majority had to work Describe the name and structure of the Spartan fighting formation - Phalanx: rows of soldiers, fight as one combined unit – shields, spears Summarize (including: who, what when, where, why, significance) the Greco-Persian wars (490s BCE) - Persians: lived east of Greece - Athens fights Persians in Greek colony in Anatolia (Darius – Persians) - Persians fight at battle of Marathon (Nike Athena!) - Persian king (Xerxes) – brings the troops to Greece - Spartans hold off at Thermopylae - Persians burn Athens – Athenians go to Salamis - Athenian navy defeats Persians – Persians go home - Greeks win, Persians don’t attack anymore What was the Delian League? When was it created and why? - 5th C BCE - (after Persian wars) defend Athens and allies against another Persian invasion Why would Athens not let members leave the League? - Money went to Athens (for buildings and naval strength), needed the money What is meant by saying that the DL was an instrument for the Athenian empire? - Used as a revenue sources for Athens, allows for Athens to prosper What is meant by “golden age of Athens?” Give examples of why Athens experienced it’s “Golden Age” during the 5th century BCE - Arts, drama, poetry, architecture, sculpture, science - Pericles ruled for 40+ years - Era great stability - Built the Parthenon Who was Alexander III of Macedon? Why was he called ‘The Great’? When did he reign? Who, what and where did he rule? Where did he conquer? - Son of Philip II - “great” because of successes at a young age - Conquered Persian empire - Defeated Darius III at Gaugamela - Reigned for 12 years, constantly fighting - Anatolia, Greece, Egypt to Khyber Pass (India) What was the Hellenistic Age? Describe the accomplishments of Greeks during this time. - Blending of Greek and Eastern cultures after AtG Be sure to include accomplishments in the arts, sciences, mathematics, etc. - Euclid: geometry - Archimedes: pi - Eratothenes: astronomy - Huge statues, steam engine, Name some famous Greek philosophers. Describe their philosophies. - Socrates - Plato - Aristotle Describe the difference between the 3 types of Greek columns. - Doric: boring straight, nondescript - Ionic: Princess Leia, circular nubs on top - Corinthian: fancy pants, ornate with leaves Roman Republic/Empire Who lived in Italy before the Romans? - Etruscans: from Asia minor – in Tuscany, north of Rome Foundation and establishment of Republic - Struggles between wealthy and poor. 509BCE last Etrus. king deposed, republic established - Rome founded by brothers: Remus and Romulus (raised by the she-wolf) brother murder Parts of the republic? Who were the consuls? What kind of powers did they have? - 2 eleceted officials – commanded army, directed government – orig: 2 Pats., veto each other - Elected every year, had to wait 10 yrs. to be elected again What was the senate? Who were these people, what powers did they have? - Dominated by Pats, life term, foreign and domestic powers, nobility - More prestigious than consuls What was the assembly? Who were these peoples? Tribunes? Who where they? - Democratic portion - Groups of commoners - At first only Pats, as time moves on more Pleb participation - Not as much power as other - Tribunes: pleb reps to lobby plebeian affairs/desires to senate Punic Wars Who fought? Why? What were the strengths of each side? How many were there? Who won? Famous generals? What was the ultimate outcome? Significance of the wars? - Rome vs. Carthage for Med Sea supremacy - 3 wars, spanned several decades - Carth: large pop., strong navy, mercenary army, wealthy trade city, old - Rome: smaller, loyal troops, up and coming on the scene, large reserves - 1st: Carth winning early, Rome comes back after learning how to fight on the water - 2nd: Hannibal: Carth/Spainiard, take elephants and destroys Italy for 13 years, Scipio Africanus goes and destroys Carthage… deciding battle: Battle of Zama turning point - 3rd: Carth – not a threat in trade or military, Rome hates and makes a smoldering mass - Sig.: Rome becomes the sole Med Sea power!!! Describe how a general could become a powerful politician - Creating a loyal military – gains political/governmental support - Bandwagonism – everyone loves a winner Describe the philosophical differences between Marius and Sulla. - Sulla: conservative, aristocratic supporter – liked the wealthy people - Marius: social reformer, land redistributer (to the poor), military general – consul many times - Fought each other for Roman rule What was the 1st Triumvirate? Who were the members? Why was this created? What did they do? What happened to the members? - Caesar, Crassus, Pompey - To get Caesar elected consul Caesar: general – Gaullic general, successful Caesar fights Pompey (P jealous of Cae’s success) Who was Julius Caesar? How did he gain power? - Caesar: roman ruler, gained power because of popularity - Named consul for life What changes did he impose? - Expanded senate - Roman citizenship to peoples outside Italy - Employed poor, distributed land to supporters - New calendar (not used anymore) He was dictator? How long? - 10 yrs., died by Brutus, Cassius - Ides of March, 44BCE (15th) - Followers kill the conspirators - Becomes 2nd triumvirate - Antony, Lepidus, Octavian Who was Augustus? What does “Augustus” mean? How long did he rule? - Octavian – defeated Antony/Cleop. - Augustus: “exalted one” - Over 40 yrs. - Started Pax Romana Describe the continual struggle between the patrician and plebeians. How did this struggle define the Republic? - Patricians (nobles) made laws - Plebeians (commoners) - Plebs revolted, wanted rights - 12 Tables: official roman laws - The continual struggle forced the wealthy to make consessions to the poor, Poor get more rights over time Describe the Pax Romana. (who what when where why?) What did it accomplish? Describe some of the technological advancements of the Romans - Period of peace and prosperity starting with Augustus’ rule - Lasted 200+ yrs. - Empire expands, population grows - Trade routes established, Rome stable - Long term planning made this period successful - Arch use, aqueducts, concrete Who split the Empire? Why did this happen? - Diocletian splits - Too big, made East/West – created the “rule of four” – tetrarchs - Made a bunch of reforms, and killed Christians Where was the new capital established? - New cap. in Anatolia Who was Constantine? What did he do? - Founder of Constantinople - Roman Emperor - 1st Christians emperor - Converted to Christianity on death bed - Put symbol (P X) on his shield Describe the decline of the Roman Empire. Why did this happen? When did it start? - After Pax Rom. ends, RE begins the decline - Disease - Economic issues: inflation - Barracks emperors – lots of people claiming the throne - Internal conflict - Trade breaks down - Basically, it was too big How did the Roman Empire fall? Who was Alaric? Who were the Visigoths? Who was the last Roman Emperor? Who was the first “non Roman” ruler? - Invaders in west Europe - Barbarians/Germanics - Odoacer – 1st non Roman Emp. - Romulus Augustulus – last Roman Emp - Alaric – Visigoth, sacked Rome 410 - 476 – Rome falls, but the East Roman Empire endures for another 1000 years. What is Christianity? What is it based on? - Religion based on teachings of Jesus - Monotheistic, religion of salvation Who was the founder? Why and how did this religion become so wide spread? Who are some vital people/events in early Christianity? - Jesus founder - Spread by apostles/missionaries - Paul: missionary spread word around Mediterranean - Council of Nicaea: decided divinity of Jesus (both divinity and human) - Bishop of Rome = Pope (Peter was 1st) - 380 become official religion of R.E. - Edict of Milan (tolerance of Christianity – 313ce) Byzantine Empire Where located? How long did it last? What was the extent of the Empire? Name of capital? - Eastern Roman Empire - Constantinople capital - Dominated eastern Mediterranean - Between Aegean and Black sea - Balkan Peninsula to middle east, to Egypt - Slowly loses territory over time List and describe some of the legacies of Justinian. Who was his wife? Why is she memorable? - Theodora – stripper wife, co-emperor - Rebuild C-ople - Hagia Sophia - Codified Roman Laws (Corpus Juris Civilis) - Sent Belisarius to reconquer west, successful for a time - Stopped a riot at Hippodrome - Ruled in the 6th c. CE Who were the major threats to the Byzantines? - Pre-Islam: Sassanids in East, Germanics in West - Islamic dynasties after 650 - C-ople captured a couple times by Muslims, but couldn’t hold it What is caesaropapism? - Emperor has political power and religious influence (but not total religious power) Who were some groups that were highly influenced by the Byz empire? - Slavs and Turks - Converted to Christianity - Rus people in the North - Prince Vladimir of Kiev - Moscow – 3rd Rome Why was the Byz empire so successful for so long after the western Roman Empire failed? - Strength of rulers, laws - Wealthy/established trade routes - Connected to east - Well protected capital - Theme system What was iconoclasm? Why did this happen? - Breaking of icons - By Leo III, thought it was a worship of false gods, against a commandment - 700s Why did the Eastern and Western Christian church split? What was this called? What were each branch named after the split? What is the name of the head of each branch? - Supremacy of high leadership (Pope vs. Patriarch) - Great Schism, 1054 - Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox - Remains split today Describe the decline of the Byz empire. Who finally conquered them? - 4th crusade in 1200s defeats C-ople - 1453 Ottoman Turks, Mehmed II finally defeats Byzs. Renames Istanbul - Byzantine empire slowly loses territory as Islam spreads from 650-1450 - All the smart people (ancient Greek scholarship) moves West (Italy), Renaissance ensues Who was Basil II? What did he do? Nickname? - BulgarSlayer! - Defeated Bulgarians in the Balkan Peninsula - Blinds them good, sends home Silk Roads Study your notes, read your chapters, study your outlines. (who what when where why how) Map From Spain to China, study the places on the final map I handed out in class. There will be map portions on the final exam.