* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Survey
Document related concepts
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
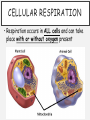
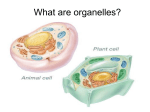
CELLULAR RESPIRATION FROM PHOTOSYNTHESIS TO CELL RESPIRATION • What are the end products of Photosynthesis? _______________________ • Why are these products important (how are they used)? _______________________________________________ WHAT IS CELLULAR RESPIRATION? It is a PROCESS ALL organisms (including plants) perform cell respiration! • Cellular Respiration is how every cell changes Glucose into ATP. ATP is the cell’s energy molecule. • ATP is used by cells to perform ALL biological activities! (STRANGER-C) CELLULAR RESPIRATION • Respiration occurs in ALL cells and can take place with or without oxygen present TWO TYPES • Cellular respiration is the process in which glucose is used to produce cell energy • This energy-releasing process takes place in ALL living cells (plant AND animal!) Two types: Aerobic - with oxygen Anaerobic - without oxygen WHAT'S HAPPENING? • During cell respiration, glucose is broken down to create a high-energy molecule called “ATP” • Carbon dioxide and water are waste products of this process • Hank - Cell Respiration SUNLIGHT TO ATP • During Photosynthesis, radiant energy is captured and stored in the bonds of Glucose • During Cell Respiration, the energy in Glucose is transferred to a molecule of Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) ATP is the energy molecule for ALL living organisms (plant AND animal) : CELL ENERGY (ATP) •ALL organisms use Glucose to create a more “usable” form of energy called ATP •ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate •ATP is the energy molecule for ALL living things! Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups CELL ENERGY (ATP - ADP) • In the Mitochondria, ATP is converted to ADP when energy is needed • ADP stands for adenosine diphosphate • Breaking a Phosphate group off of ATP releases the energy that is stored in that bond Adenine Ribose 2 Phosphate groups ATP TO ADP AND BACK AGAIN • All energy is stored in the bonds of compounds —breaking the bond releases the energy • When the cell has energy to store it adds a phosphate group to ADP - producing ATP • When the cell needs energy for life processes, it breaks the bond holding the phosphate group and changes ATP back to ADP • Adding a bond stores energy • Breaking a bond releases energy ATP TO ADP AND BACK AGAIN • It’s almost like recharging your cell phone! AEROBIC CELLULAR RESPIRATION • In most Eukaryotic organisms, cell respiration requires oxygen. • This is aerobic cellular respiration. • In aerobic respiration, glucose is broken down completely into ATP, carbon dioxide and water. • This is an efficient process which makes 36 ATP molecules from one Glucose molecule. aerobic exercise FORMULA FOR AEROBIC CELL RESPIRATION C6H12O6 + O2 ----> H2O + CO2 + 36 ATP – 1 Glucose molecule and 2 ATPs are needed to start the process – Aerobic (with oxygen) is very efficient! 1 Glucose makes 36 ATP molecules! Do you notice something about this equation? O2 + C6H12O6 H2O + CO2 + ATP • It’s the opposite of the Equation for Photosynthesis! CO2 + H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + O2 PLANTS AND ANIMALS RELY ON EACH OTHER! • Animals use: • Glucose (from producers/plants) • Oxygen (from producers/plants) • Plants use: • Carbon dioxide (from consumers/animals) • Water (from consumers/ animals) WHERE DOES THIS HAPPEN? • Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria. (That's why we call this organelle the “mighty mitochondria – because it is the “powerhouse” of the cell!) mighty mouse saves the day • Mitochondria are found in both plant and animal cells. **Cells that need more energy (muscle cells) have more mitochondria** THE MITOCHONDRIA CHANGE THE O 2 AND GLUCOSE O2 O2 O2 O2 O2 INTO CO 2 , H 2 O, AND ATP GLYCOLYSIS • Before aerobic cellular respiration can occur, an initial step, called glycolysis, takes place outside the mitochondria, in the cytoplasm • What do the letters “LYS” stand for???? __________________ • “GLYC” stands for glucose… • What do you think Glycolysis means? _______________________________ GLYCOLYSIS • The Mitochondria are covered by a selectively permeable membrane • Glucose is too big to fit through the pores • In Glycolysis, the Glucose molecule is broken into two molecules of Pyruvate Remember…Glyco stands for “Glucose”... “lys” means destroy • This occurs in the cytoplasm GLYCOLYSIS • Remember Diffusion???? • In order for the molecule to DIFFUSE, it has to FIT through the membrane! • So… Glucose has to be chopped in half! • It becomes two molecules of Pyruvic Acid (Pyruvate) GLYCOLYSIS ?? ?? ?? ?? ?? Which is a ?? bigger, more ?? ?? complex ?? molecule? ?? In glycolysis, Glucose is broken down so it can diffuse into the mitochondria. GLYCOLYSIS… • Glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvate (aka pyruvic acid) • This step occurs before either anaerobic or aerobic cellular respiration • 2 ATP are needed to “chop” glucose! • The pyruvate then enters the mitochondria, where aerobic cellular respiration occurs AEROBIC CELL RESPIRATION • There are two steps which happen after glycolysis: • The Krebs cycle, or citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain (ETC) • Both happen inside the mitochondria • Overall, at the end of these three steps, there is a net gain of 36 ATP molecules. KREBS CYCLE • The Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) requires oxygen • This is where Carbon Dioxide is formed • Think: Krebs = Carbon • This part of the process takes place in the mitochondria ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN (ETC) • Electrons are passed through the membrane of the mitochondria • They bind with 2 H+ ions and Oxygen to form a molecule of H2O • Remember? Bonding through dehydration synthesis! ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION • When there is no oxygen, cell respiration consists of two pathways: • Glycolysis and Fermentation. • Both of these occur in the cytoplasm and only produce 2 ATPs ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION • Anaerobic Respiration is also called Fermentation • 2 Types: Alcoholic & Lactic Acid ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION • Fermentation is used in the baking and brewing industries • It occurs with yeast and bacteria, but will occur in animals (humans) under certain conditions • Depending on the organism, there are different end products from the breakdown of glucose ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION EQUATIONS (FERMENTATION) • In Plants (Yeast): • Pyruvate ---> Alcohol + CO2 • In Animals (Bacteria & Muscle Cells): • Pyruvate ---> Lactic Acid IN PLANTS (YEAST) • Yeast is used in the baking and brewing industries • To make Bread, Beer and Wine • As yeast perform anaerobic respiration, they convert glucose into ethanol alcohol with CO2 as a bi-product Bacteria & Muscles…. • Bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Bacteria convert glucose into lactic acid • The same happens in overworked muscle cells! • Ever feel the “burn” in your muscles after working out??? • That’s Lactic Acid! IN ANIMALS (HUMANS!!!!) • Ever run in gym class and feel a burning in your legs? • How about lifting weights? Do your arm and chest muscles ever burn while you are working out? • That burning sensation is muscle fatigue – and it's caused by lactic acid build-up! MUSCLE FATIGUE • During exercise, muscle cells use oxygen faster than your body can supply it! • To get more energy, the muscle cells convert to anaerobic respiration • This causes a build up of lactic acid in the muscle tissue – acid “burns” and your muscles feel “sore” REVIEW QUESTIONS • What is cell respiration? ________________________________ ________________________________ • The waste products of aerobic cell respiration are: ______________ & _______________ • The energy from glucose is transferred by cell respiration into energy molecules called ___________ • In what organelle does cell respiration occur? ____________ MORE.... • The process of _______________ cellular respiration does NOT require oxygen. • The process of _______________ cellular respiration DOES require oxygen. • Another name for anaerobic cell respiration is ____________________. • The end products of fermentation are • ____________ & either ____________ OR _____________