* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20 – Circuits and Circuit Elements
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Invention of the integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Digital electronics wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
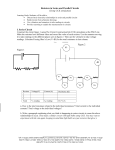
Chapter 20 – Circuits and Circuit Elements Schematic Diagrams and Circuits pg 731 know the symbols for each of these components of a circuit (a path for electrons to follow) What is a circuit? Pg 732 for definition Does a lightbulb offer a complete conducting path? What are the components of a lightbulb? (a): charges enter at the base (b): go thru filament (c): exit at threads Series Circuits Resistors in series have the same current – all charges must flow through each resistor The equivalent resistance in a series circuit is the sum of all of the circuits’ resistors: Req = R1 + R2 + R3 + ….. The Req is always greater than any individual resistance Series circuits require all elements to conduct – if one resistor is broken, no current can flow and everything stops Parallel Circuits Resistors in parallel always have the same potential difference (∆V) across them There is more than one path for the charges to flow The sum of the currents in parallel circuits equals the total current: Ieq = I1 + I2 + I3 + … The equivalent resistance is a reciprocal relationship: 1/Req = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + … Complex Circuits Resolve by isolating parts of a complex circuit until the equivalent resistance is found….. Homework: Practice 20-A Odd Practice 20-B Odd Practice 20-C Odd Practice 20-D Odd